CYSTINE: WHAT IS IT?
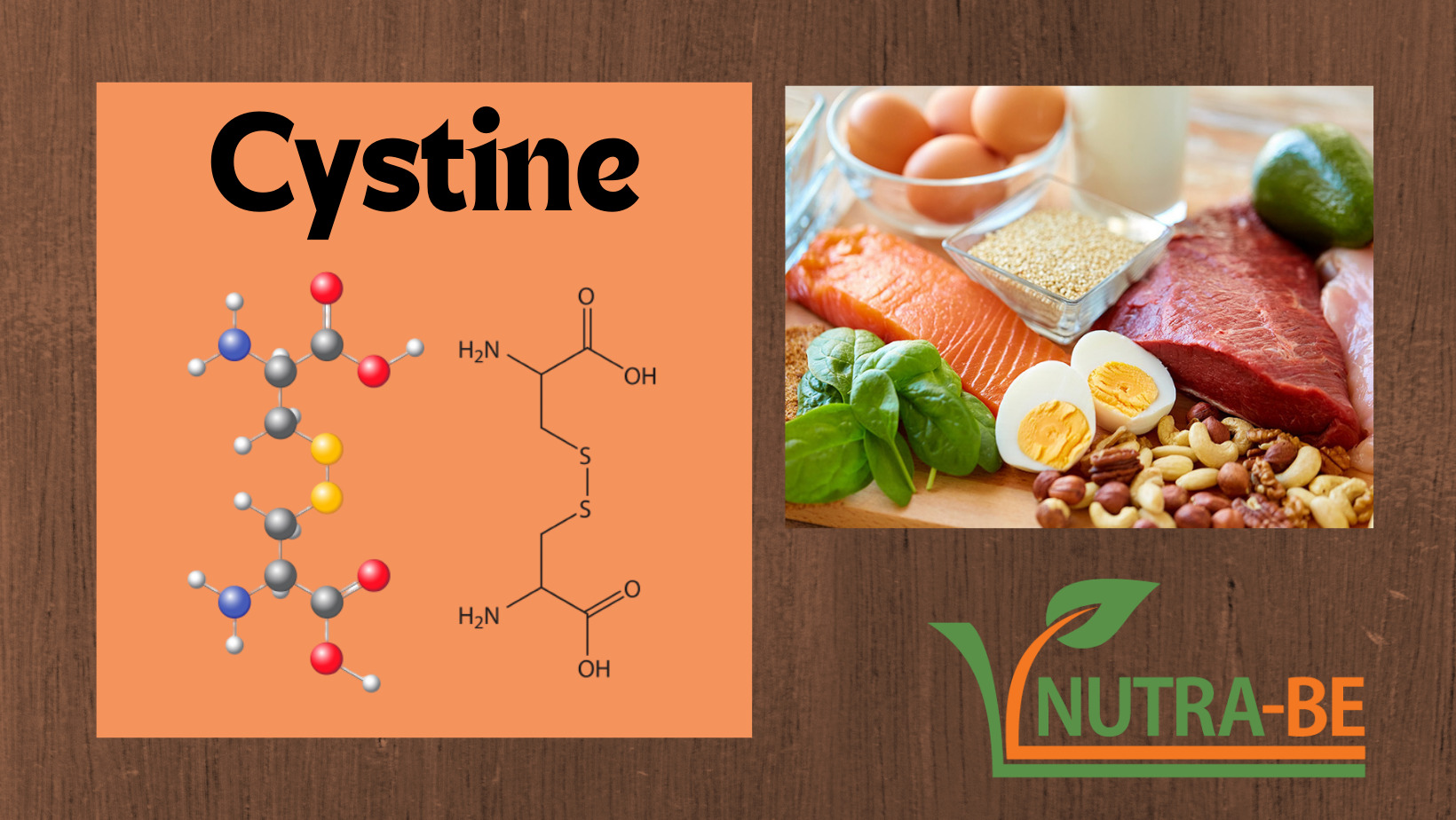
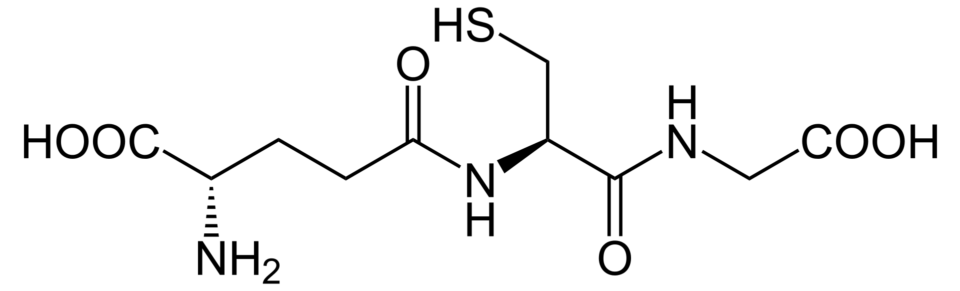
Cystine is a sulfur-containing amino acid, with the molecular formula C6H12N2O4S2, obtained by the oxidative reaction of two cysteine molecules. It appears as a colorless solid, with a melting point of about 260°C.
Cystine was discovered in 1810 by William Hyde Wollaston, but it was recognized as a protein component only in 1899, when it was isolated from the horns of a cow.
In fact, cystine is present in many proteins and it significantly affects their tertiary structure.
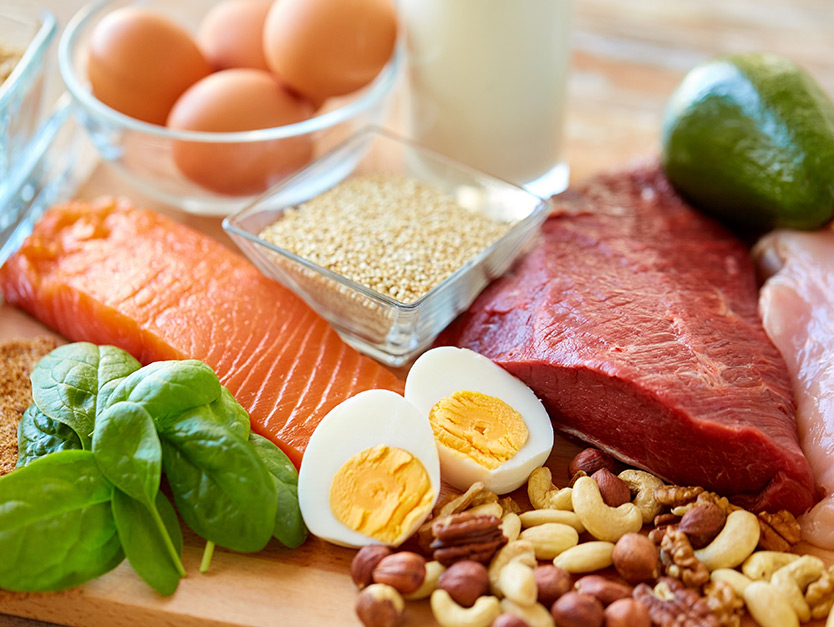
CYSTINE IN FOOD
From a dietary point of view, the main sources of cystine are:
| Food | Quantity of cystine g/100g |
| egg white powder | 2,102 |
| soy isolate proteins | 1,15 |
| egg powder | 1,099 |
| mustard seeds | 0,68 |
| cod in salt | 0,673 |
| dried spirulina algae | 0,662 |
| dried egg yolk | 0,614 |
| raw bran | 0,576 |
| soybean flour | 0,556 |
| dry yeast | 0,5 |
| whitefish | 0,5 |
| dehydrated fish eggs | 0,499 |
| dried nuts | 0,462 |
| wheat germ | 0,458 |
| caviar | 0,449 |
| lupini beans | 0,446 |
Cystine is not digested or hydrolyzed significantly in the stomach, but it is transported by the blood flow to the various cellular districts of the body: here the weak disulfide bond is split and cysteine is produced.
ROLE OF CYSTINE
Cystine is mainly used as a source of cysteine by the body.
In the last twenty years, the studies on the use of cysteine in the medical field have increased a lot. To date, multiple uses of cysteine are known:
- antioxidant activity: cysteine is a precursor of the synthesis of glutathione, an important and powerful antioxidant, whose reduced form plays a fundamental role in the defense of cells from oxidative stress.
- hair reinforcement: cysteine is one of the main components of keratin, one of the most abundant proteins in the skin and hair. In fact, cysteine forms disulfide bridges, giving keratin greater strength and rigidity.
- strengthening of the immune system.
- protection of the digestive system: cysteine strengthens the lining inside the stomach and the intestine, so that the absorption of proteins useful to the body can take place at best.
- mucolytic action: the sulfhydric group of cysteine has the ability to break the bridges of glico-proteins that are in the mucus, favoring its fluidization, reformation and consequently its elimination.
CYSTINE DEFICIENCY
A moderate cystine deficiency in the human body usually generates an unexplained increase in weight and low levels of fundamental proteins in the blood.
When the deficiency becomes severe, more evident and worrying symptoms are added to the mild ones, such as:
- depigmentation of the scalp.
- extreme and inexplicable fatigue.
- liver damage.
- muscle weakening.
- impoverishment of the epidermis, with spontaneous appearance of skin lesions.