MELATONIN: WHAT IS IT?
Melatonin, chemically called N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine, is a hormone produced by the pituitary gland, a gland located at the base of the brain, which exerts its action on the hypothalamus, regulating the sleep-wake cycle in humans and animals.
It is also produced by plants: however, in this case, it only has an antioxidant function.
MELATONIN IN FOOD
Melatonin is present in significant quantities in several foods, including:
| Food | Quantity of melatonin picograms/1 g |
| Oats | 1700 |
| Corn | 1400 |
| Tomatoes | 600 |
| Radishes | 500 |
| Cherries | |
| Bananas | |
| Grape | |
| Rice and cereals | |
| Plums | |
| Olive oil | |
| Wine | |
| Beer |
THE ROLE OF MELATONIN
In animals and humans, melatonin has the function of regulating
- sleep-wake rhythm
- blood pressure
- seasonal reproduction
- immune system
The substance’s main task is undoubtedly the regulation of the sleep-wake cycle. Indeed:
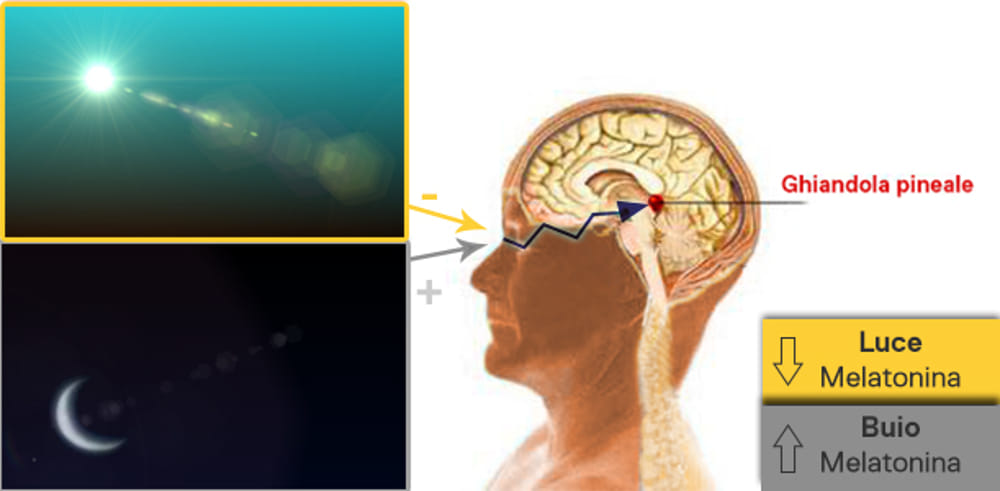
with darkness, the pituitary gland produces more melatonin, a signal that is interpreted by the body as impending rest.
With light, on the other hand, melatonin production decreases and thus the body prepares to stay awake.
MELATONIN SUPPLEMENTS
Melatonin is used as a supplement or as an actual drug to regulate the sleep-wake cycle, especially in cases of:
- jet-lag
- professions with night shifts
- blind subjects
- general insomnia
- delayed sleep phase syndrome (DSPS)
- insomnia related to attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
- insomnia caused by beta-blockers
- sleep problems in children with developmental disorders, such as autism, cerebral palsy and mental retardation
The use of melatonin is intended to improve sleep duration and quality.
It also has a number of advantages:
- absence of effects in the morning, such as drowsiness and dizziness
- no development of tolerance with repeated doses over time
- no development of dependence
- high tolerability, with few side effects
The data in the literature refer to the administration of doses of between 0.3 and 5 mg per day: however, in the European Union, it is stipulated that in the case of self-medication (without a doctor’s prescription), the dose of 1 mg per day of melatonin must not be exceeded.
MELATONIN DEFICIENCY
Melatonin production decreases with aging. During the night, the reduced levels of the hormone that are released can contribute to the problem of insomnia and early awakening. Melatonin production has a seasonal pattern, with shorter periods of production in summer and longer periods in winter. The presence of a light source during the night can block melatonin production and can cause sleep disturbances.